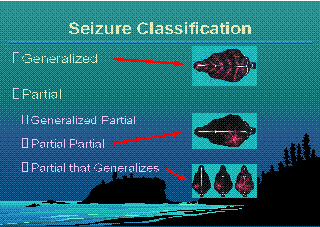
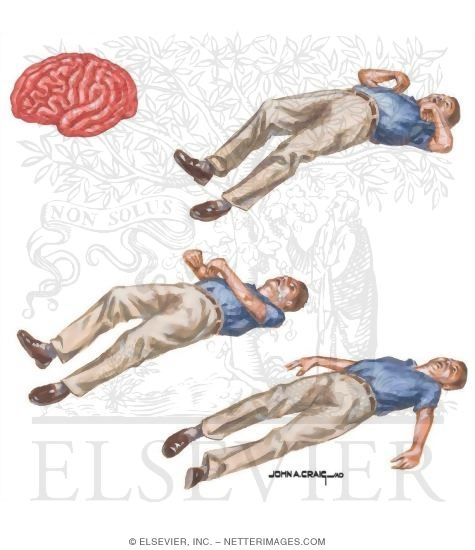
Generalized Seizures
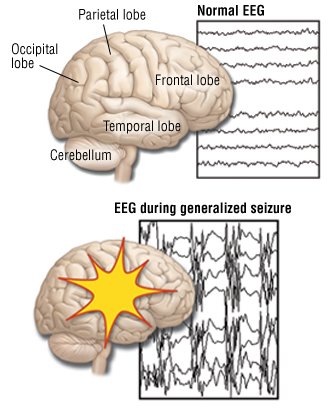
Generalised epilepsy, also known as primary generalised epilepsy or idiopathic epilepsy, is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalised seizures, as opposed to partial seizures, are a type of seizurethat impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain (which can be seen, for example, on electroencephalography, EEG). Generalised epilepsy is primary because the epilepsy is the originally diagnosed condition itself, as opposed to secondary epilepsy, which occurs as a symptom of a known as diagnosed condition. Generalised seizures can be either absence seizures, myoclonic seizures, clonic seizures, tonic-clonic seizures or atonic seizures. Generalised seizures occur in various seizure syndromes, including myoclonic epilepsy, familial neonatal convulsions, childhood absence epilepsy, absence epilepsy, infantile spasms (West's syndrome), Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.





No comments:
Post a Comment